CAD-Q
Quantifying the Cost of Poor CAD Model Quality in Industry and Developing Strategies for Improvement based on Formal Modeling Methodologies (CAD‑Q)
Grant PID2022-137254OB-I00 funded by:

The proposal
High-quality parametric CAD models can be defined as 3D models that are free from geometric and topological errors, can be modified without causing regeneration errors that may hinder reusability, and properly convey design intent. In this context, low-quality models incur significant financial costs, and companies struggle to quantify their impact.
This project aims to address this gap by assessing CAD quality issues, proposing formal modeling methodologies, and developing supporting tools. Methods include qualitative and quantitative research, including user activity tracking and analysis of modeling logs. Leveraging recent research, the project seeks to define systematic strategies for creating high-quality models. Tools will be implemented to evaluate model reusability, regeneration performance, and design intent preservation.
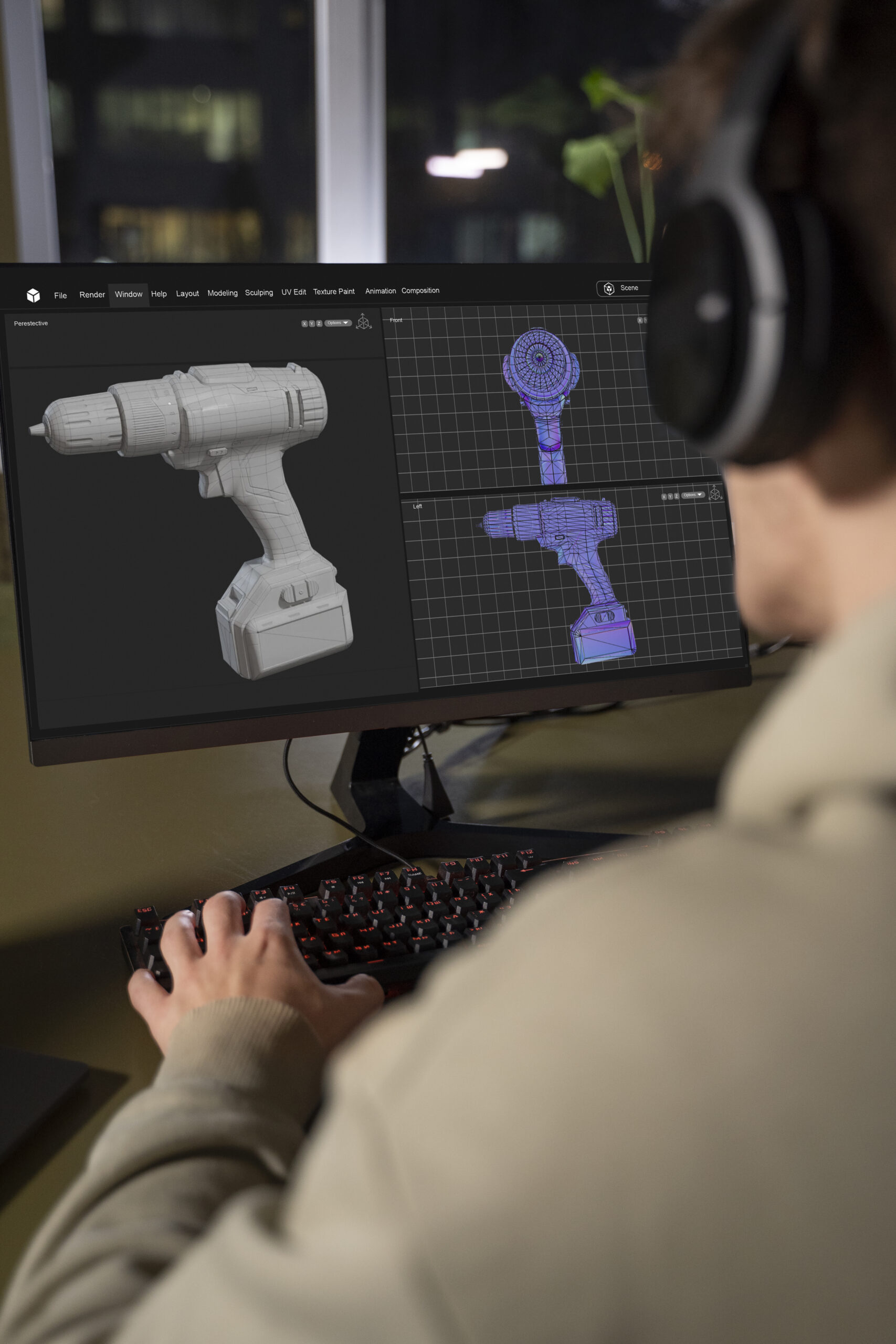

This project has been selected in the grant call of the State Program to Boost Scientific and Technical Research and its Transfer, of the State Plan for Scientific, Technical, and Innovation Research 2021-2023. It falls within the regulatory framework approved by Order CIN/1025/2022, and has been a beneficiary of the early processing call for the year 2022 for the grant procedure for knowledge generation projects and pre-doctoral training.
105.700 €
Hypotheses
The starting hypotheses of the project are (1) HS1, the cost of low-quality CAD models is a relevant problem in industry, and (2) HS2, the formal modeling methodologies developed in CAD-Q for solid and surface models result in significantly higher quality CAD models than available methodologies. These hypotheses are novel as they depart from the well-known but often ignored fact that low-quality CAD models cost time and cause failures with high economic impact. There is little literature on this problem because companies are generally reluctant to openly discuss the prevalence of low-quality models in their organizations.

Methodology
In order to test the postulated hypotheses, a methodology has been designed based on the objectives outlined below. First, the research team will be conducting web questionnaires and semi-structured interviews with CAD professionals to determine the scope of CAD quality-related problems in industrial settings. The research team will interpret participants’ responses, acknowledging inherent subjectivity. The project’s remaining objectives are supported by a research strategy inspired by Design Science and Action Research Methodologies. This includes analyzing existing methodologies, developing new modeling methodologies based on findings, and iteratively refining them. The selected commercial CAD systems for methodology application are DS Solidworks and Siemens NX.
Objectives

Determine the scope and size of CAD quality-related problems in industrial settings through qualitative and quantitative research methods, developing a formal model of costs.

Elaborate a proposal of formal modeling methodologies for the creation of high quality solid and surface models in parametric feature-based CAD systems.
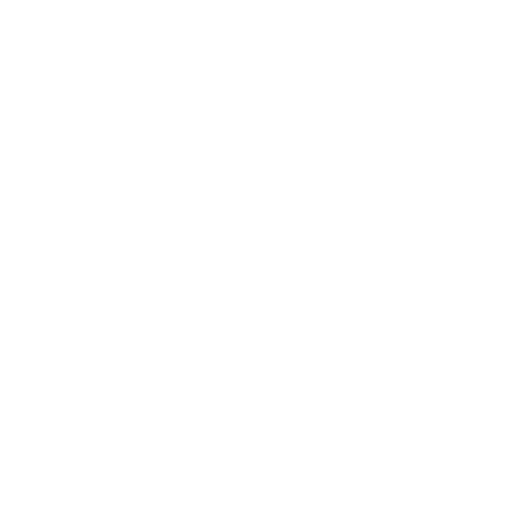
Implement tools to support the development and validation of formal modeling methodologies.

Disseminate the results of the project to the scientific community and transfer the results to industry.
The project will address four general objectives. These general objectives are further detailed in the next link.
Results
The CAD-Q project aims to address significant gaps in the generation of scientific-technical knowledge within the realm of 3D CAD modeling, particularly focusing on its impact on Industry 4.0 initiatives. By conducting the first international study on the economic repercussions of low-quality 3D CAD models in industrial settings, CAD-Q seeks to shed light on this critical issue.
Through qualitative and quantitative research methods, the project endeavors to provide valuable insights into the scope and magnitude of problems associated with poor CAD quality. Dissemination of findings through scientific and professional channels will raise awareness and support for further research in this field, countering misconceptions that it is a resolved issue. Moreover, CAD-Q aims to bridge the current research gap by offering formal modeling methodologies and validation frameworks for creating high-quality 3D CAD models. This information will be freely accessible to stimulate advancements in CAD technology and promote collaboration within the international research community.
Furthermore, the project aligns with the thematic priorities outlined in the State Plan for Scientific, Technical, and Innovation Research 2021-2023, focusing on digital transformation and industrial transition. By fostering collaboration with key stakeholders and industry associations, CAD-Q aims to maximize the societal and economic impact of its results, ultimately contributing to sustainable economic growth, industrial resilience, and technological innovation. Through comprehensive plans for scientific communication, internationalization, dissemination, and transfer of results, CAD-Q seeks to establish itself as a cornerstone in the field of Product Data Quality, reinforcing the international network of collaboration and promoting gender-inclusive research practices.
Researchers
Our proposal aims to generate synergies between three different institutions, Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Universitat Jaume I (UJI) and Mondragon Unibertsitatea (MU) that share a vision focused on quality around CAD technology. In this conext, Dr. Manuel Contero and Dr. Pedro Company are the lead researchers of the project, but there are more people working alongside them with an outstanding background. If you want to know more about our team, please, press the bottom below.

Manuel Contero
Dr. Contero is a Full Professor with the Graphic Engineering Department at UPV, Valencia (Spain). He earned an MSc degree in Electrical Engineering in 1990 (UPV, Spain) and a PhD in Industrial Engineering in 1995 (UPV, Spain). In 1993 he joined UJI as Assistant Professor, promoting to Associate Professor in 1997. In 2000 he returned to UPV, being appointed Full Professor in 2008. His research interests focus on sketch-based modeling, collaborative engineering, human computer interaction, development of spatial abilities, and technology enhanced learning.

Pedro Company
Dr. Company is a Full Professor of Graphic Expression in Engineering at UJI. He graduated as an Industrial Engineer from the UPV, Valencia (Spain) in 1985, and obtained his PhD in Mechanical Engineering in 1989. In 1994 he joined UJI as Associate Professor, promoting to Full Professor in 1996. His research interests focus on computer-aided design, computer graphics, and sketch-based modeling, with over 50 published articles and research communications in these areas. Additionally, he has been actively involved in research related to Emotional Design and Collaborative Product Engineering.
Send us a message
Come visit us!
UNIVERSITAT POLITÈCNICA DE VALÈNCIAEscuela Técnica Superior de Ingeniería Industrial, Universitat Politècnica de València, Camino de Vera, s/n, 46022 Valencia (Valencia), España